Market and Supplier Analysis of New Energy Vehicle Drive Motors and Inverters
With the continuous increase in the penetration rate of global automotive electrification, the drive motor industry will experience rapid expansion in overall scale. During this process, third-party motor manufacturers with economies of scale and technological advantages will have the opportunity to rapidly expand their market share and achieve significant growth in performance.
According to estimates, with the rapid advancement of global automotive electrification, the market for new energy vehicle motor systems will expand rapidly, and the market size is expected to grow from $2.3 billion in 2015 to $31.8 billion in 2030.
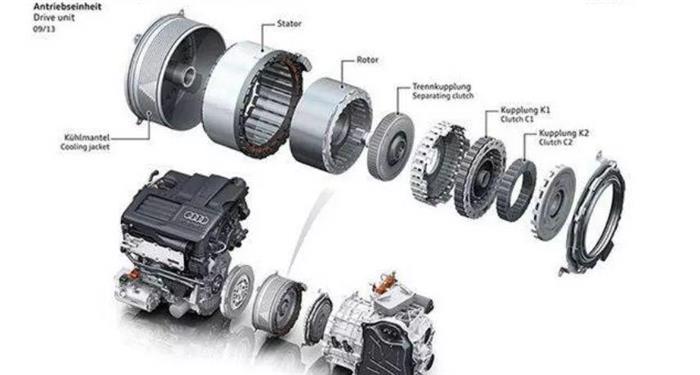
The motor system of new energy vehicles mainly includes two parts: the electric motor and the inverter. Although these two parts, like most other automotive components, have long faced price pressure, the overall industry still has significant room for growth due to the increase in the total number of new energy vehicles. We expect the average annual growth rate of the market size to be around 18% -20% by 2030.
In terms of system unit price, the overall development of motor systems towards high power has also brought about an increase in assembly prices.
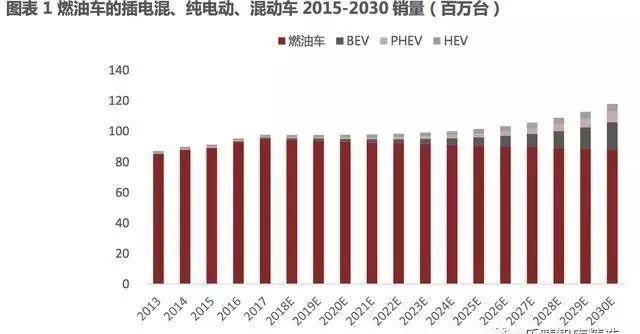
According to estimates, under neutral assumptions, the sales of electric vehicles will reach 20 million units by 2030, accounting for approximately 16% -18% of the total passenger car sales for that year. However, in an optimistic scenario where battery prices significantly decline and environmental policies become more stringent, the growth rate of electric vehicle sales may increase significantly. We expect that in an optimistic scenario, the total annual sales of new energy vehicles may reach the level of 30 million units, accounting for about 25% -27% of the annual car sales.
The expected power demand for a single motor hybrid car is around 30kw (with an average price of about $200- $300), for a dual motor plug-in hybrid car it is about 50-100kw (with an average price of $800- $1000), and for a pure electric car it is about 200kw (with an average price of $1000- $1500).
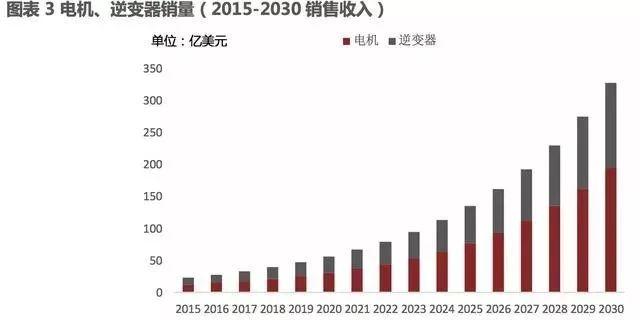
We expect the average annual growth rate of electric motor (excluding inverters) sales to reach 18% by 2030, and the overall industry sales to reach $19.5 billion by 2030, nearly 17 times the level of $1.2 billion in 2015.
It is expected that the sales of electric motors will increase from 3.6 million in 2015 to 49 million in 2030. At the same time, the number of motors per vehicle is expected to decline from 1.8 to 1.4, mainly due to the increase in the proportion of pure electric vehicle sales with single motors.
But we expect the unit price of electric motors to further increase, from the current $350 to $380, mainly driven by the wider application of high priced high-power motors.
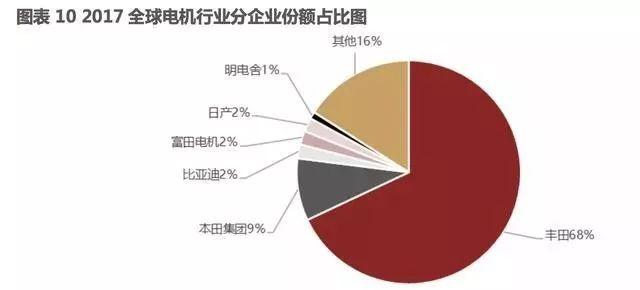
From the perspective of market share, Toyota Group was far ahead in 2016 data (the main companies producing electric motors in the group include Denso and Aisin Precision Machinery), while Honda Group ranked second. At the same time, both groups also hold global leading positions in the hybrid field. Next are BYD and Taiwan's electric motor manufacturer Futian Electric, which supplies Tesla.
In the long-term development process of the motor industry, the rise of third-party suppliers will be the trend. If we observe the current situation of the Japanese automotive industry chain, it is not difficult to find that the top three leading companies (Toyota, Honda, Nissan) tend to supply their own electric motor products, which is not only related to the traditional genes of Japanese manufacturing enterprises, but also to the stage of industry development.
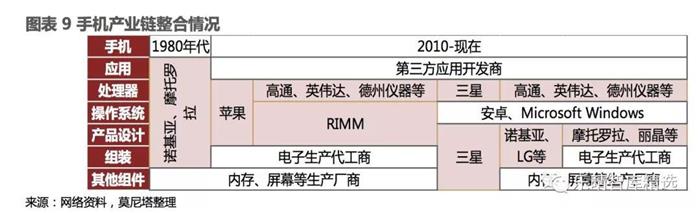
If we compare the development history of the PC and mobile phone industries, it is not difficult to find that both industries were highly integrated in upstream and downstream production in the early stage. Whether it is HP, Apple, or Silicon Graphics in the PC industry, or Nokia and Motorola in the mobile phone industry, they are highly integrated in the industry chain. Because the product update and replacement speed is fast in the early stage, upstream component suppliers need to respond quickly and cooperate with each other, so the integrated production mode has a high cost-effectiveness;
However, in the later stages of industry development, due to the expansion of the entire market size and the slower pace of product updates, the scale effect of third-party suppliers targeting the entire market as their customers is reflected. This has also given rise to a series of third-party suppliers such as Foxconn, Micron, and Hynix.
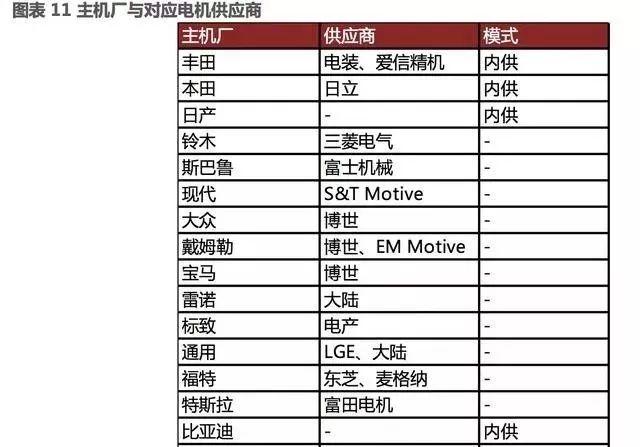
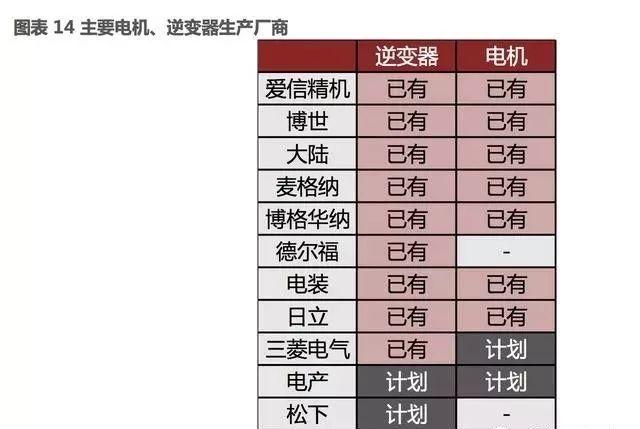
The new energy vehicle motor industry is no exception. From the current point of view, Honda has announced that it will cooperate with Hitachi to produce motors. At the same time, Nissan also mentioned at the investor exchange meeting that it may start outsourcing electric motors in the future.
In October 2017, Mitsubishi Electric announced that it would provide motors and inverters for Daimler Benz. With the popularity of high-performance and low-cost products from third-party motor manufacturers, the market share of the motor industry is shifting from self supply by host manufacturers to third-party enterprises, which is a trend.
Currently, Japanese motor companies have started to respond to the trend shift brought about by electrification. We expect Denso and Aisin Precision Machinery to first leverage their existing scale advantages and occupy market share at lower costs, followed closely by Denso and Mingdian.
At present, the average gross profit margin of the motor industry is around 30%, and production scale is one of the main factors determining the high or low gross profit margin.
We predict that the inverter industry will also experience rapid growth. According to estimates, the sales revenue of the inverter market will increase from $1.2 billion in 2015 to $13.3 billion in 2030.
In terms of sales, as the ratio of inverters to motors is basically 1:1, it is expected that their total sales will increase from 3.6 million in 2015 to 49 million in 2030.
At the same time, the price of bicycle accessories will decrease from $300- $400 to $200- $300, mainly due to the cost scale effect after the increase in quantity.
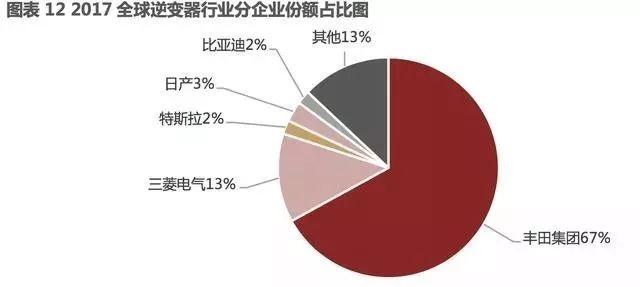
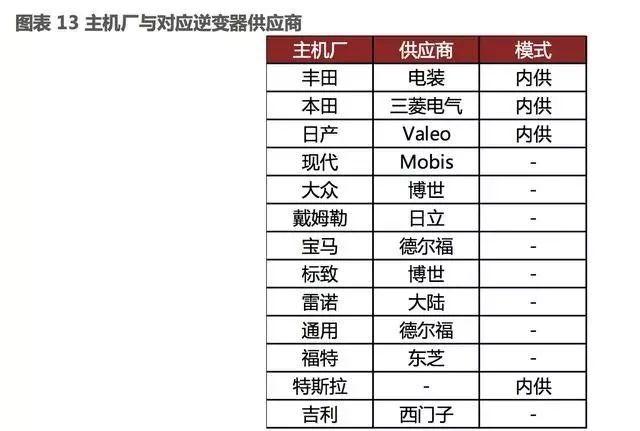
Similar to the field of motors, Toyota Group currently holds a leading position in the inverter industry. Meanwhile, Denso Group, a subsidiary of Toyota Group, is currently expanding its inverter customer base on a large scale. After Toyota, Mitsubishi Electric also holds a considerable market share.
From the classification of motors, there are mainly four types: DC, AC induction, permanent magnet synchronous, and switched reluctance. New energy vehicle motors mainly use the latter three types.
Currently, permanent magnet synchronous motors are the mainstream type due to their superior performance. The price of AC asynchronous motors is moderate, but their performance is slightly inferior, and some manufacturers in the United States and China use them. The main advantage of switched reluctance motors is their lower price, but there are also technical issues of noise and vibration. If these problems can be solved, switched reluctance motors will have a large market.
AC asynchronous motor: Although currently, AC asynchronous motors (rated power around 79-85) do not have advantages in terms of power compared to permanent magnet synchronous motors, their cost is much lower than that of permanent magnet synchronous motors. In terms of size, AC asynchronous motors are larger than permanent magnet synchronous motors, mainly due to design and construction limitations.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor: The motor has a rotor wrapped with permanent magnets inside, and the overall system power is relatively high (around 90-92), while the volume is relatively small. The cost is relatively expensive, mainly due to the high price of permanent magnet materials. At present, research is being conducted on reducing the use of permanent magnets, while also focusing on improving the output efficiency of magnets. Permanent magnet motor is currently the most widely used type of motor in the electric vehicle motor industry.
Switched Reluctance Motor: Switched Reluctance Motors are very competitive in price, mainly due to the absence of high cost permanent magnets in their rotors, and their moderate power (rated power around 80-86). Due to the use of the tension between the stator and rotor to provide power, vibration and noise caused during the process are the main issues. Due to the rapid increase in demand for electric vehicle motors, we believe that the rise in demand will accelerate technological innovation and substitution.
By studying the technological evolution trends of motors over the past 20 years, we have found that there is still significant room for further improvement in motor technology. Firstly, check the thickness of the steel used in the movement. For the stator and rotor, they are mainly composed of thin electromagnetic steel layers stacked together. In 1997, the first generation Toyota Prius used a 0.35mm steel layer, which was later reduced to 0.3mm and recently to 0.25mm in 2016. Generally speaking, increasing the number of thin steel layers can increase motor efficiency and also help control motor temperature.
At present, manufacturing thin steel is a major technical challenge in the industry. The main difficulty lies in controlling the rebound in die casting and maintaining the consistency of steel sheet materials. From the current situation, rotary forging technology will increasingly become the mainstream manufacturing method in the industry due to its advantages in cost and production efficiency.
Secondly, in terms of winding density, the overall amount of winding in the stator is an important factor determining the power of the motor. The main factor determining the amount of winding is the number of turns that copper wire can be wound around the core within a limited space. In terms of technology, the current use of inserters is suitable for high-power stator processing and has gradually become a standard in industry production.
In terms of coil types, there are mainly two types: square and circular. Currently, mainstream manufacturers use circular coils, but square technology is gradually replacing circular coils as the industry trend due to its high space utilization. Toyota and Honda have started to adopt square winding technology in bulk. On the other side, Yaskawa Electric has started developing electronic winding technology with the aim of improving control and efficiency (Mazda has already started trials).
Finally, in terms of the cooling system, it is divided into two parts: the motor and the inverter. As the temperature of the motor increases, the magnetic force of the permanent magnet motor will weaken, so the efficiency of the cooling system is crucial for high-power operation of the motor.
From the perspective of technological evolution trends, mainstream cooling technologies have evolved from air cooling and water cooling to the current stage of oil cooling. The main technical method is to immerse the motor into an oil cooling chamber to achieve the purpose of cooling. Although some experts believe that friction with oil can reduce the efficiency of the motor, considering various factors, oil cooling is still the most effective cooling mode under current technological conditions.
In terms of inverters, the cooling system is equally important for the performance of the inverter. Nissan recently claimed that in the 2017 Lingfeng new model, by improving the inverter cooling system, the output power of the motor was increased from 80kw to 110kw, while other parts of the motor were the same as the previous generation.
This reflects the importance of the inverter cooling system. Although the use of silicon carbide will improve the heat and pressure resistance of motors, its high cost may make it difficult to achieve large-scale application in the short term.